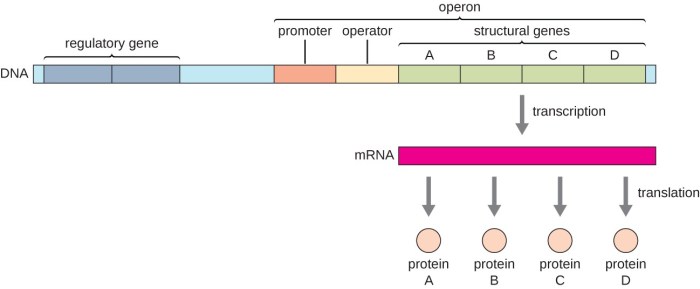
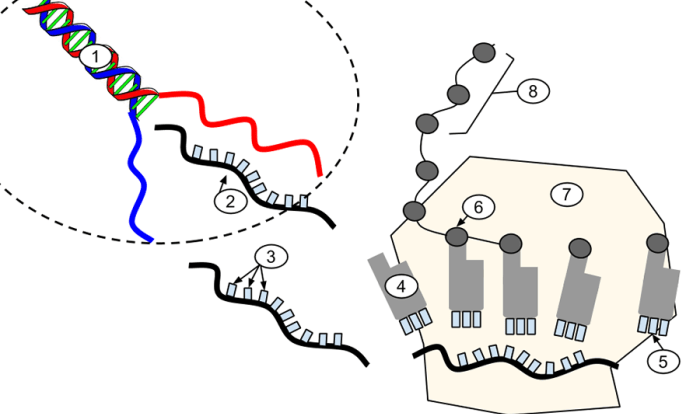
Embark on a scientific odyssey with Gene Expression Translation POGIL Answers PDF, a comprehensive guide that unveils the intricacies of gene expression. This meticulously crafted resource delves into the molecular mechanisms underlying the translation of genetic information into functional proteins, providing a profound understanding of the central dogma of molecular biology.
Within these pages, you will discover the pivotal roles of mRNA, tRNA, and ribosomes in the translation process, deciphering the genetic code that governs the synthesis of proteins. Moreover, the document explores the dynamic regulation of gene expression, highlighting the diverse mechanisms that control the timing, location, and abundance of protein production.
Gene Expression Translation
Gene expression translation is the process by which the information encoded in a gene is used to produce a protein. The process involves several steps:
1. Transcription: The DNA sequence of the gene is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule by an enzyme called RNA polymerase.
2. mRNA Processing: The mRNA molecule undergoes several modifications, including splicing and addition of a poly-A tail, to make it ready for translation.
3. Translation: The mRNA molecule is transported to the ribosome, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome, which are then linked together to form a polypeptide chain.
4. Protein Folding: The newly synthesized polypeptide chain folds into a specific three-dimensional structure, which is essential for its function.
Regulation of Gene Expression
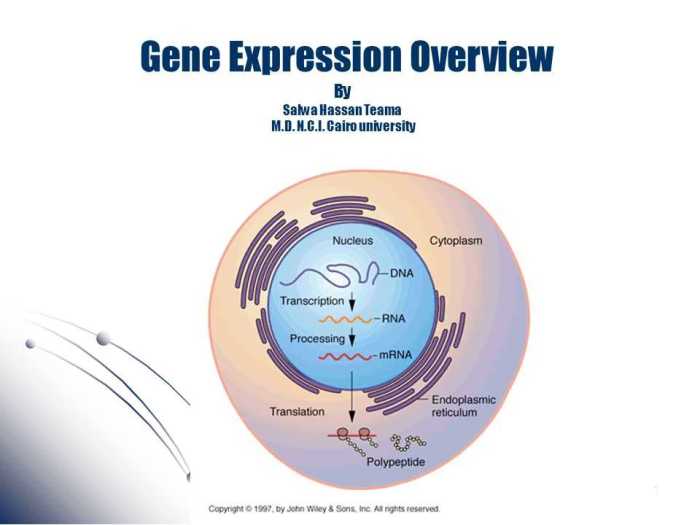
Gene expression is tightly regulated to ensure that the right proteins are produced at the right time and in the right amount. Several mechanisms are involved in gene regulation:
Transcriptional Regulation, Gene expression translation pogil answers pdf
- Promoter Regions:Genes have specific promoter regions that bind transcription factors, which control the initiation of transcription.
- Enhancers and Silencers:Enhancers and silencers are DNA sequences that can bind proteins and either enhance or repress transcription.
- Epigenetic Modifications:Chemical modifications to DNA and histones can affect gene expression without altering the DNA sequence.
Translational Regulation
- MicroRNAs (miRNAs):miRNAs are small RNA molecules that can bind to mRNA and prevent its translation.
- Ribosomes:The availability and activity of ribosomes can affect the rate of translation.
- Protein Kinases:Protein kinases can phosphorylate translation factors and inhibit translation.
Post-Translational Regulation
- Protein Degradation:Proteins can be degraded by proteasomes or other enzymes.
- Protein Modifications:Proteins can be modified by phosphorylation, glycosylation, or other chemical changes, which can affect their stability, activity, or localization.
Gene Expression and Disease
Disruptions in gene expression can lead to a variety of diseases:
- Genetic Mutations:Mutations in genes can alter the structure or function of proteins, leading to disease.
- Dysregulation of Gene Expression:Dysregulation of gene expression can occur due to environmental factors, cellular signaling defects, or epigenetic changes.
Examples:
- Cancer:Cancer cells often have mutations or dysregulation of genes involved in cell growth and proliferation.
- Cystic Fibrosis:Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene, which leads to defective chloride transport in the lungs.
Gene Therapy:Gene therapy aims to correct genetic defects by introducing functional genes into cells.
Gene Expression Analysis Techniques
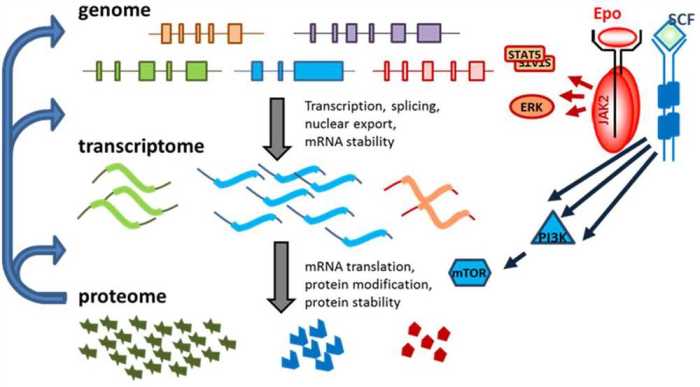
Various techniques are used to analyze gene expression:
RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction)
RT-PCR is a technique used to amplify and quantify specific mRNA molecules. It involves converting mRNA into complementary DNA (cDNA) using reverse transcriptase and then amplifying the cDNA using PCR.
Microarrays
Microarrays are high-throughput platforms that allow the simultaneous measurement of the expression of thousands of genes. They involve hybridizing labeled mRNA or cDNA samples to complementary DNA probes on a chip.
RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq)
RNA-Seq is a high-throughput sequencing technique that allows the quantification and analysis of all RNA molecules in a sample. It provides a comprehensive view of the transcriptome.
Gene Expression Databases and Resources: Gene Expression Translation Pogil Answers Pdf
Publicly available gene expression databases provide a wealth of information for research purposes:
- Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO):A repository of gene expression data from various experiments.
- The European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) Expression Atlas:A comprehensive resource for gene expression data across different species and tissues.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Gene Expression Database:A database of gene expression profiles from various organisms.
These databases facilitate data sharing and collaboration among researchers, enabling a deeper understanding of gene expression and its implications in health and disease.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of the genetic code?
The genetic code is a set of rules that determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein based on the sequence of nucleotides in a gene.
How does a ribosome participate in translation?
Ribosomes are cellular structures that assemble amino acids into proteins according to the instructions encoded in mRNA.
What are the different levels of gene regulation?
Gene regulation can occur at the transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels, controlling the production and function of proteins.